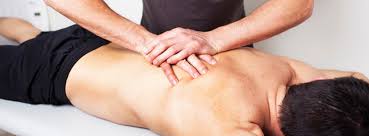
Physiotherapy, often referred to as physical therapy in some regions, is a physiotherapy mayfair healthcare discipline that utilizes movement, manual techniques, and evidence-based interventions to support, rehabilitate, and enhance the human body’s function. In an era where lifestyle-related ailments and sports injuries are on the rise, physiotherapy serves as a critical pillar in preventative care and rehabilitation, fostering recovery and overall wellness.
The Essence of Physiotherapy
At its core, physiotherapy emphasizes the dynamic interplay between movement and health. It is grounded in the understanding that the body is an intricate network where movement not only signifies health but is also essential for healing. Physiotherapists, through advanced training and practical experience, diagnose and manage conditions that affect physical performance—ranging from musculoskeletal dysfunctions to neurological impairments—while also advising on preventive measures.
Key Principles:
- Individualized Treatment: Every patient is unique. Physiotherapists assess a patient’s history, movement patterns, and functional limitations to tailor interventions that promote optimal recovery.
- Evidence-Based Practice: Treatments are grounded in scientific research and clinical experience, ensuring that the techniques used are both safe and effective.
- Holistic Approach: In addition to physical symptoms, physiotherapy often addresses factors such as pain management, psychological well-being, and lifestyle modifications, ensuring comprehensive care.
The Spectrum of Physiotherapy Techniques
Physiotherapy encompasses a rich variety of treatment modalities designed to improve mobility, strengthen muscles, and relieve pain. The diverse methods are adapted to the specific needs of each patient, ensuring targeted interventions for various conditions.
Common Techniques Include:
- Manual Therapy: This technique involves hands-on manipulation of muscles and joints. Techniques such as mobilization, soft tissue massage, and trigger point therapy are often used to reduce pain, improve circulation, and enhance flexibility.
- Exercise Prescription: Therapeutic exercises are a cornerstone of physiotherapy. Customized exercise programs target muscle imbalances, improve coordination, and increase strength. These exercises can be performed in clinics or at home, ensuring continuity of care.
- Electrotherapy: Advanced modalities such as transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), ultrasound, and laser therapy are employed to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and promote tissue healing.
- Movement Reeducation: Techniques focusing on gait training, posture correction, and balance enhancement are vital for patients recovering from neurological disorders or injuries.
- Hydrotherapy: The unique properties of water—buoyancy, resistance, and temperature—are harnessed to deliver low-impact treatments that facilitate movement and reduce joint stress, especially beneficial for older adults and patients with arthritis.
Application Across Diverse Health Challenges
Physiotherapy is not a one-size-fits-all solution but rather a customizable approach applicable across a wide range of health conditions.
- Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation: Whether recovering from a sports injury, joint replacement surgery, or chronic back pain, physiotherapy plays a pivotal role in restoring function and alleviating discomfort. Strengthening weak muscles, improving joint stability, and restoring range of motion are critical components in these recovery journeys.
- Neurological Conditions: For patients suffering from strokes, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, or spinal cord injuries, physiotherapy can significantly enhance mobility and coordination. Techniques tailored to neuroplasticity help in the retraining of movement patterns and the recovery of lost functions.
- Pediatric Physiotherapy: Children with developmental delays, congenital disabilities, or post-injury impairments benefit tremendously from interventions aimed at enhancing motor skills. Child-friendly techniques and play-based therapies not only support physical development but also integrate learning and social interaction.
- Cardiopulmonary Rehabilitation: After cardiac events or respiratory conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), physiotherapy provides structured exercises to improve cardiovascular performance, strengthen respiratory muscles, and increase overall endurance.
- Sports-Specific Training: Athletes often require specialized physiotherapy to maintain peak performance, prevent injuries, and speed up recovery. Sports physiotherapists bring together biomechanical insights and conditioning programs that enhance performance while minimizing injury risk.
The Impact of Physiotherapy in Modern Healthcare
Physiotherapy’s contributions extend well beyond the confines of rehabilitation clinics. It is an integral component of holistic healthcare that supports both acute and chronic care needs.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: By managing pain, improving mobility, and restoring function, physiotherapy significantly enhances the quality of life for patients of all ages.
- Preventive Health: Through targeted exercise regimens and education, physiotherapists empower individuals with the knowledge and tools to prevent injuries and manage chronic conditions proactively.
- Multidisciplinary Collaboration: Physiotherapists often work in tandem with physicians, occupational therapists, and other healthcare professionals to ensure that patient care is cohesive and comprehensive.
Embracing Innovation: The Future of Physiotherapy
The evolution of physiotherapy is closely tied to technological advancements and ongoing research. Emerging technologies such as virtual reality, wearable devices, and tele-rehabilitation platforms are revolutionizing the way physiotherapy is delivered. These innovations allow for:
- Remote Assessments and Treatment: Telehealth and video conferencing enable physiotherapists to provide guidance and monitor patient progress from a distance, making care more accessible.
- Data-Driven Insights: Wearable technology captures real-time data on movement patterns, pain levels, and recovery progress, allowing for more personalized treatment plans.
- Enhanced Learning and Simulation: Virtual reality tools can simulate complex environments, aiding patients in retraining their motor functions in safe and controlled settings.
Conclusion
Physiotherapy stands at the intersection of science, movement, and individualized care. It is a discipline that not only addresses the physical manifestations of injury and disease but also contributes significantly to overall well-being and quality of life. Whether it is restoring mobility after an injury, managing chronic pain, or preventing future complications through proactive care, physiotherapy provides a pathway to healing through movement and innovation. As healthcare continues to evolve, the role of physiotherapy becomes ever more crucial in guiding patients toward healthier, more active lives.